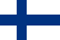
Osteochondrosis is a chronic disease of cartilage tissue in which the degenerative-dystrophic process predominates.The disease can affect any joint in the body, but most cases occur in the intervertebral disc.Depending on the location, osteochondrosis of the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine is distinguished.The peak incidence is observed at the age of 30-40 years, but recently the disease has become younger and occurs even in teenagers.Symptoms similar to osteochondrosis occur in 50-90% of the population.In this article, you will find the main symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis and methods of treating this disease.
Specific osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is less common than other types.The anatomy of the thoracic spine includes more discs than the lower and neck combined.However, this disc is inferior in size and thickness.Due to the redistribution of the load on the ribs and sternum, this part of the spine is less mobile.
Although for intervertebral osteochondrosis in the lumbar region a more characteristic symptom is pain after excessive and inappropriate physical activity, for the thoracic region pain is practically atypical.Often, symptoms of complications of various diseases of the cardiovascular system or respiratory system are observed.
Because of development
The most common cause of osteochondrosis is an inactive lifestyle.Nowadays, people have to work at the computer in the most uncomfortable position for their back.Also, lack of physical activity affects the condition of the muscles on which the condition of the intervertebral disc depends.Not only physical inactivity, but also excessive physical activity can cause osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine;The following risk factors were also identified:
- descent;
- Various forms of spinal curvature, such as scoliosis, posture disorders;
- inactive lifestyle, inactive work;
- excessive physical activity or sudden cessation of active sports;
- spinal cord injury;
- bad habits, chronic stress, insomnia;
- overweight, obesity;
- flat feet, wearing uncomfortable shoes;
- Dystrophic changes associated with the body's normal aging process.
Recently, there is a trend towards the rejuvenation of this disease.Symptoms of osteochondrosis are diagnosed starting in adolescence.There is a hypothesis that this is due to a lot of time spent on the computer.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is quite clear, but can be hidden under other diseases or their complications: attacks often resemble myocardial infarction, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, or renal colic.Among the most common are:
- The occurrence of acute pain after a long stay in one position, most often uncomfortable.This pain also appears in response to sudden movements or due to lifting heavy weights;
- There may be no pain, but a feeling of tightness in the chest or back.Difficulty breathing, pain on deep inspiration or breath;
- Due to damage by osteochondrosis to the nerve roots emerging from the spinal canal, numbness or tingling sensations can be observed in certain areas of the body;
- There is also a dull pain in or between the shoulder blades, and also in the shoulder girdle and sternoclavicular joint;
- Lower leg coldness is caused by blood supply complications.
Some general, non-specific symptoms may occur:
- Frequent attacks of intercostal neuralgia;
- From the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, heartburn, bloating, flatulence, constipation or diarrhea.Abdominal pain may occur as a result of damage to the lower segment of the thoracic spine;
- peeling skin, thin and brittle nails and hair;
- Disorders of the reproductive system.
Often the symptoms show themselves in the form of vertebral syndrome: dorsago and dorsalgia.This is the main marker of this disease, which often indicates osteochondrosis of this department with 100% probability.
Dorsago
Characterized by sudden sharp pain in the thoracic spine.Patients associate it with "knife" pain, because in most cases, it is acute and unbearable.Often, the cause of this type of pain is a long sitting position or an uncomfortable posture.When trying to stand or take a more comfortable position, a person experiences acute pain, or "lumbago," which can also cause restriction of movement for some time.
Dorsalgia
This type of pain has a gradual onset with cumulative effects and can develop over 2-3 weeks.With dorsalgia, pain or discomfort is observed in the localization of the damaged area of the spine.When changing body position or deep breathing, the pain increases significantly.There is a tendency for the pain to intensify in the evening or after physical activity.In the morning, patients usually note weakness or loss of pain.Short walks also help.
Diagnostics
Making a diagnosis for any pathology begins with a comprehensive examination of the person and analysis of his complaints about his condition.For example, in advanced stages, often the curvature of the spine, which is noticeable from the outside.On the other hand, if the posture is affected, it should be carefully examined for the presence of osteochondrosis.It is recommended to carefully analyze the hereditary prerequisites of the patient for the development of this pathology.It is necessary to refer the patient to undergo a general blood and urine test.
One of the most necessary stages is radiography of the thoracic spine in various projections, with the necessary help to analyze osteophytes, their presence and size;assess the height of the disc and the presence of changes in it;size and position of the hernia.
Another X-ray method is discography, which uses a contrast agent.This allows you to assess the condition of the nucleus pulposus.Computed tomography can also be used, but due to the high radiation exposure of the patient, it is used in exceptional cases.
Electrocardiography is a mandatory examination method.The symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine are very similar to the symptoms of myocardial infarction and angina pectoris.
Treatment
To successfully treat osteochondrosis of the spine, it is necessary to influence the cause of the disease, and not limit yourself to painkillers only or immediately send to surgery.For example, a patient with low mobility will receive a completely different treatment approach compared to a patient with a history of spinal cord injury and its complications.It is also very effective to combine therapy methods to enhance and consolidate their effects.
Medicines
In the period of acute illness, in addition to medication, strict bed rest is recommended.The main group of drugs for breast osteochondrosis:
- analgesics for acute pain relief;
- For some patients, the use of antispasmodics is recommended;
- B complex vitamins;
- Chondroprotectors, which require individual selection for each patient, taking into account the characteristics of the development of the disease, as well as taking into account the specifics of the development of the body.
Drug therapy is only effective in the early stages of the disease.In addition, in the form of chronic osteochondrosis, the drug can be prescribed for life or until complete recovery.
Exercise therapy
Exercise therapy is therapeutic physical culture.Today there are many useful exercises for the prevention and treatment of osteochondrosis in the thoracic region.This includes breathing exercises as well.
The basis of exercise therapy for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is the board.You should start it with a minimum time, increasing it every day to a minimum level.The goal is 1.5 minutes.Also in this position, it is recommended to alternately press your knees to your chest, holding this position for 5-10 seconds.It is also useful to try to hang on the horizontal bar with the same gradual increase in time.
The method of exercise therapy is used outside the period of acute illness and is one of the most universal methods that can be combined with others.
Manual therapy
Manual methods affect the musculoskeletal system to relieve chronic and acute pain in the joints and spine.It also helps increase the range of motion in the joints and correct postural disorders.Also used to relieve muscle tension.
Manual therapy also helps improve blood circulation in the intervertebral disc and improves the transport of oxygen from the blood to the tissues and vice versa.In this way, it is possible to eliminate osteochondrosis complications related to damage or compression of blood vessels, as well as lack of oxygen in tissues and organs.
Traditional method
The advantage of traditional medicine is that its effects have been tested for many years.There are many ways to treat any disease at home without the risk of side effects.Recipes for infusions used for diseases:
- Calendula.Take 100 g of product per 200 ml of regular men's cologne.Add some camphor oil.Leave in a cool and dark place to incubate for two weeks in a tight bottle;
- Dandelions.Take dandelion root, mint leaves, birch buds and coriander, 2 tablespoons each.L. and pour 0.5 cups of boiling water.Cook on low heat for 2-3 minutes, stirring constantly.After this, add 60-70 g of butter and cook for another 20 minutes, and then cool.
It is very important to rub these decoctions tightly on the affected area of the chest.Rubbing should be done with gentle massaging movements for 5 minutes.Then protect the rubbing area, for example, with a sweater.All decoctions are stored in the refrigerator.
Some herbs are not approved for use in the presence of certain diseases, so it is better to consult a specialist.
First aid for worsening
First of all, it is necessary to heat the painful area.But you only need to do this with medical ointment;You can not use decoctions: there is a chance to get skin burns.
It is best to do this with a light heating cloth, for example, a woolen product.Then it is recommended to lie on a hard surface to correct the uneven body position.In a pinch, even the floor will do.In case of enlargement of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, use a tight bandage to the chest.
During an attack, it is advisable to take painkillers, preferably intramuscularly.NSAIDs are used for acute attacks.
If there is no improvement in your well-being within 30-60 minutes, then you must call an ambulance and be sure to inform them upon arrival about the pain medication.
Prevention
Prevention is the easiest and least expensive way to maintain health.Every person exposes himself to many negative environmental factors every day.If this effect is minimized, then the chances of developing osteochondrosis are reduced to zero.Basic principles for the prevention of thoracic osteochondrosis:
- Lead an active lifestyle.It's easy to overdo it and put more stress on your spine.It is better to listen to the needs of the body, start with a minimum load and gradually get used to it.Morning jogging and swimming pools are most optimal for this.
- Monitor prolonged sitting in one position.It is best to regularly stretch the upper shoulder girdle joints, try to maintain proper posture, and rest your shoulders.
- You can't skimp on chairs for sitting work.Let it be a special chair that supports the spine well.
- Use an orthopedic mattress and pillow.It is during sleep that the spine most often becomes deformed, remains in a curved position for a long time, and then disappoints with pain and discomfort throughout the day.This is the initial prerequisite for osteochondrosis.Better to warn them.
- Avoid carrying heavy objects.Unfortunately, sometimes this is important.In this case, it is better to ensure the distribution of weight over the body.And try to do everything smoothly, without sudden movements.Otherwise, this may threaten not only osteochondrosis.
- Wear comfortable shoes.In everyday life, heels will only bring health problems.It is better to put it to see the evening.
- Strengthens muscles.Abs, lower back, back and spine muscles.This is the main framework for healthy and correct posture.
We must not forget proper nutrition.The daily menu must meet the needs of the individual body and include the maximum amount of vitamins, micro and macroels.
Conclusion
- Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is a dystrophic-degenerative disease in which deformation and loss of function of the vertebral disc occurs.
- Thoracic osteochondrosis is less common than this type of pathology.Recently, this disease has been diagnosed not only in the elderly, but also in teenagers.
- There are many factors in the development of this disease.As a rule, osteochondrosis begins due to several reasons.
- Monotherapy is rarely effective.To eliminate the cause and symptoms of the disease, treatment tactics are developed, including taking medication, exercise therapy and other additional procedures.
- Simple prevention can reduce the development of osteochondrosis of the breast to a minimum.